

What are Varicose Veins?
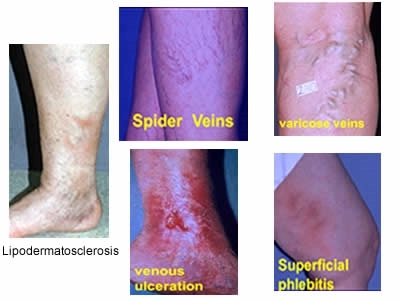
Varicose Veins are enlarged, tortuous veins seen in the legs and feet. They may occur as small spider veins or may become extremely enlarged. Varicose veins progress over a period of time, later giving rise to symptoms and may be responsible for multiple complications in some patients.
Symptoms of Venous Veins insufficiency:
- Leg pain, aching or cramping
- Burning or itching of the skin
- Leg or ankle swelling
- Heaviness of legs
- Swelling in the ankles
- Open wounds or sores
- Skin pigmentation around the ankles
- Skin discoloration or texture changes
- Venous ulcers (non-healing wounds) around the ankles
- Rupture of veins and bleeding
- Development of clot formation (thrombosis)
Risk Factor of Venous Veins insufficiency:
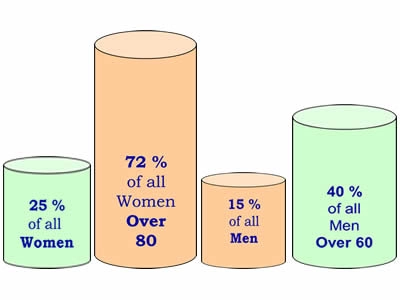
- Gender
- Age
- Heredity
- Pregnancy
- Standing occupation
- Obesity
- Prior injury or surgery
- Sedentary lifestyle
Why Do Varicose Veins Develop?
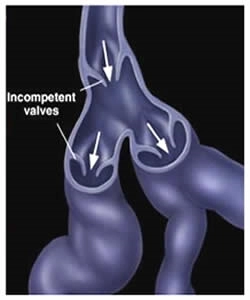
Leg veins carry blood from the legs to the heart against gravity. These veins have many one-way valves, so that the blood goes up towards the heart only, and not downwards. If these valves are damaged, on standing up or sitting, the blood in the veins will now flow down into the legs due to the effect of gravity, leading to gradual dilatation and enlargement of the veins, leading to Varicose Veins.

Veins carry blood up to the heart

Incompetent vein valve
Leaking valves lead to vein enlargement

Blood going up Cannot come down
Common Sites Of Vein Valve Leakage Leading To Varicose Veins
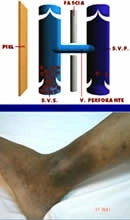
Perforator Vein Valves Leakage
Valves in the communicating veins between the superficial and deep veins leak giving rise to dark skin around the ankles

Indicates advanced Venous Insufficiency
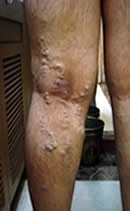
Sapheno Popliteal Valve Leakage
Behind the knee joint. The short saphenous vein gets dilated from the knee to the ankle
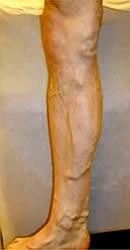
Sapheno Femoral Valve Leakage
At the groin. Leads to enlargement of great saphenous vein from the groin to ankle

Anterior Circumflex Vein Reflux
Doctors Will Gauge The Severity Of Varicose Veins By The CEAP Method
“C” = Clinical Condition
- C0 – no visible venous disease
- C1 – telangiectasias or reticular veins
- C2 – varicose veins
- C3 – edema
- C4 – skin changes without ulceration
- C4a – pigmentation or eczem
- C4b – LDS or “atrophie blanche”
- C5 – skin changes with healed ulceration
- C6 – skin changes with active ulceration

